Foreign Trade
Foreign/International Trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders
Types of International/Foreign Trade
| Export Trade | Import Trade | Entreport Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Sales of goods and services to another country | Purchases of goods and services from another country | Importing with the purpose of re-exporting |
| Foreign exchange enters the country | Foreign exchange leaves the country | No effect on foreign exchange |
Visible and Invisible Trade
| Visible Trade | Invisible Trade |
|---|---|
| Sales of goods to another country is called visible export | Sales of services to another country is called invisible export |
| Purchases of goods from another country is called visible import | Purchases of services from another country is called invisible import |
Why Foreign Trade has increased?
- Gap between the rich and poor countries has increased.
- Role of IMF (International Monetary Fund), SDR (Special Drawing Rights) decreases the risk of foreign exchange fluctuations.
- WTO (World Trade Organization).
- Improvement in technology has led to increased production.
- Improvement in aids to trade.
- Globalization.
- Improved standards of living.
- Efforts of governments to improve trades.
- Role of trading blocs e.g ASEAN.
Problems in Foreign Trade
- Different languages and culture.
- Additional cost of transportation.
- Additional cost of packing and insurance.
- Excessive documentation.
- Government rules in importing country.
- Import and export duty.
- Different units of measurement.
- Trade barriers like trade embargo and strict quota.
- Payment can be delayed.
- More risks involved.
- Exchange rate fluctuations.
Risks in Foreign Trade
Economic risks
- Risk of insolvency of the buyer,
- Risk of protracted default - the failure of the buyer to pay the amount due within six months after the due date
- Risk of non-acceptance
- Surrendering economic sovereignty
- Risk of Exchange rate
Political risks
- Risk of cancellation or non-renewal of export or import licenses
- War risks
- Risk of expropriation or confiscation of the importer's company
- Risk of the imposition of an import ban after the shipment of the goods
- Transfer risk - imposition of exchange controls by the importer's country or foreign currency shortages
- Surrendering political sovereignty
- Influence of political parties in importer's company
Advantages of Foreign Trade
- A greater variety of goods and services become available.
- Local shortages can be complemented.
- Government earns revenue (by import/export duties).
- More foreign exchange reserves (in case of export).
- A country can specialize in producing certain goods and services.
- Links between countries develops.
- More employment is created (All three sectors in case of export and tertiary sector in case of import).
- Increases competition and thus quality of local production.
Disadvantages of Foreign Trade
- Loss of employment in Primary and Secondary sector in case of import.
- Loss to the local producers.
- Loss of foreign exchange (in case of import).
- Importing country can become dependant.
- Dumping can occur (selling products at a loss).
- Harmful goods can enter the country.
- Increase in price level.
- Exploitation of importing country.
- Depreciation of currency of importing country.
Balance of Trade
- Difference between the visible exports and visible imports is called balance of trade.
- If visible exports exceeds visible imports than it is favorable and if visible imports exceed visible exports than it is unfavorable.
Balance of Payments
- It is the summary of a country’s total payments and receipts with the rests of the world.
- It includes all items of visible trade, visible trade and capital movement.
- If total payments exceed total receipt then it is called balance of payment deficit, which is undesirable.
- If total receipts exceed total payments then it is called balance of payment surplus, which is desirable.
Why deficit in Balance of Payments and Balance of Trade is undesirable
- Loss of foreign exchange.
- Depreciation of currency.
- Imports will become expensive and it can create inflation.
How to protect from imports-to make balance of payment surplus?
- Tariffs or duties – imposing import duties on goods to make them more expensive than home produced goods.
- Quotas – imposing limits on the amount of imports allowed into a country in a given year.
- Embargoes/Import ban – total exclusion of certain types of goods. This is often applied to harmful goods e.g. firearms.
- Exchange control – limiting the amount of currency that can leave the country.
- Increased documentation and bureaucracy at point of entry – making importing more difficult by increasing the rules and regulations for imports.
- Giving subsidies to local producers.
- Exchange control.
Steps to be taken in Exporting
- Market research for:
i. Size of market.
ii. Competitions.
iii. Economy of importing country.
iv. Government policies..
v. Public Demand. - Signing contract with buyer.
- Getting order from importer.
- Preparing the consignment.
- Mode of transportation.
- Preshipment inspections.
- Dispatch of cargo.
- Getting payment.
Documents in Foreign Trade
Indent
Issued by: Importer
Issued to: Exporter/Agent
Purpose: It is a order for goods. It gives full particulars and conditions as regards price, packing and shipment etc.
Shipping Note
Issued by: ExporterIssued to: Port Authority
Purpose: To request port authority to load the goods to be exported, specifying the quantity of goods and vessel on which goods are to be boarded. Sent together with goods and sometimes before goods are send so that space is reserved for them.
Bill of Lading (BOL) or (B/L)
Issued by: Master of ship in triplet.
Issued to: Exporter, Importer, Shipmaster.
Purpose: Acknowledging that specified goods have been received on board as cargo for conveyance to a named place for delivery to the consignee who is usually identified
Importance:
- Document of title.
- Contract of carriage.
- Receipt of goods.
- Importer cannot release the cargo from its port unless he has the bill.
- Exporter can get bank loan against the dispatched cargo upon presentation of documents including bill of lading.
- Required by custom authority for appraisement of cargo and for verifying quantities.
- It is also a document of transfer, being freely transferable but not a negotiable instrument.
Information:
- Name of exporter.
- Name of importer.
- Name of agent.
- Full details of goods.
- Place of departure and place of arrival of goods.
- Name of ship carrying goods.
Consignment Note
Issued by: Trucking company (Goods forwarder).
Information: Quantity and description of goods being dispatched.
Purpose: Evidence of contract.
Airway bill
Issued by: Airway company.
Purpose: Same as consignment note, in case of air transportation.
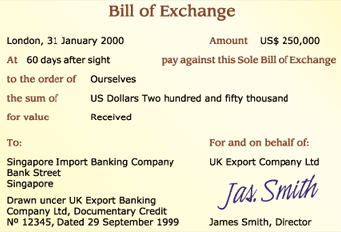
Bill of Exchange
|
 |
Finances to the Exporter
Loans and overdraft
- Granted by the bank , payable within two years, on the insurance.
- If exporter defaults making payments because importer has not paid the money then bank will claim insurance from government.
Negotiating and discounting bill of exchange
- If the exporter has bill of exchange of future maturity date, then exporter can ask his bank to release payment against the bill of exchange signed by the importer and other shipping documents.
- Bank will discount the bill at the prevailing rate and give the exporter money less than the face value of the bill.
- On maturity of bill of exchange, the exporter has to pay in full to the bank.
Finance to the Importer
Documentary Credit (letter of credit) or (L/C) or (D/C)
- It is issued by the importer’s bank to pay an overseas exporter against the exporter’s shipping documents.
- Importer goes to his bank to open a letter credit in the favour of exporter.
- Issuing bank will then send a copy of letter of credit to the exporter’s bank.
- Exporter will study the letter and make sure that they are inline with the terms and conditions.
- If terms are obeyed then exporter will prepare the goods for delivery and get all required export documents.
- Exporter will dispatch goods to importer and submit all the export documents to his bank.
- Bank will study the documents, make sure they comply with terms of letter of credit and pay the exporter.
- On delivery of goods importer has to pay money to his bank (issuing bank).