Customer Credit
Credit is an arrangement by which a buyer can take possession of something now and pay for it later or over time.
Reasons for giving Credit
- To gain competitive edge.
- To earn additional money.
- To sell a very expensive items.
- When the product sales is on decline.
Matters discussed in agreement
- Details about the buyer and seller.
- Details of the asset to be bought/sold.
- Amount of finance.
- Repayment period.
- Monthly installment.
- Interest rate charged.
- Collateral security involved.
- Rights and responsibilities of both parties.
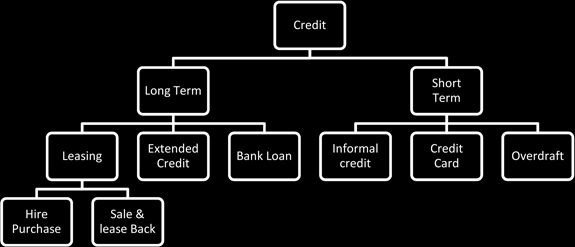
Short Term Credit
- The amount of credit is low.
- Credit is to be paid within one year.
Informal Credit
- Credit is given without any written agreement.
- Does not involve collateral security.
- Small amounts are involved.
- Repayment is to be made within one year.
- Normally offered by the retailer to their trustworthy customer.
Credit Cards
|
 |
- Advantages:
- Advantages to Card Holder:
- Increases purchasing power.
- Minimum cash handling.
- Obtain cash at ATM.
- Can be canceled when stolen.
- Postponement of payment.
- Advantages to Bank:
- Interest from card holder.
- Commission from retailer.
- Advantages to Retailers:
- More sales.
- Competitive edge.
- Minimum cash handling.
- Advantages to Card Holder:
- Disadvantages:
- Disadvantages to Card Holders:
- Limited acceptability.
- Interest is charged.
- Irrational buying.
- Every one can not have this facility.
- Can be misused.
- Disadvantage to Bank:
- Recovery of money from defaulters.
- Disadvantages to Retailer:
- Commission and rental to be paid to the bank.
- Problem of limited cash.
- Disadvantages to Card Holders:
Over Draft
- A short term facility offered by the bank to the its customers where the borrower
can over draft (withdraw money more than their balance) their accounts maintained with the banks. - Available only for current accounts.
- Used by businesses to manage cash flow problems.
Long Term Credit
- Amount of Credit is large.
- Repayment goes beyond one year.
- Repayment is made in installments.
- A written agreement is singed.
- Collateral security are involved.
Leasing
- A rental agreement which involves a series of fixed payment (annuity) which is extended to several period.
- Lessor: One who owns the asset and lets other (lessee) use it.
- Lessee: One who gets procession of the asset for its use.
Hire Purchase
- A leasing agreement in which the lessor lets the lessee use an asset for a certain time period (less that the life of the asset) upon a certain installment (rental) with an option to purchase the asset by paying the amount or return the good to lessor,
after the lease period. - Suitable for asset with good resale value.
- The lessor will own the asset till the last installment has been paid and the total value of the asset is recovered.
Sale and Lease back
- Lessee originally owns the asset.
- The asset is sold to the lessor on the bases of market price and lessee gets the full amount in lump sum.
- Title will be in the name of lessor.
- Possession will remain with lessee.
- Lessee is liable to pay installments to the lessor as per agreement.
- Lessee can not sell the asset till the installment are paid and asset comes under his ownership.
- If lessee faults in making payments lessor has the right the repossess the asset.
Extended Credit/Deferred payment
- It is suitable for items with low resale value.
- In this case customer will become owner after signing the agreement and making payment of front and fee.
- Customer can sell the asset any time.
- Loans are secured by a collateral security.
- If customer defaults making payment the financer has the right to sue him.
Comparison between Bank Loan and Leasing
| Bank Loan | Leasing | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cheaper source of finance | Expensive source of finance |
| 2. | Collateral security is involved | Collateral security is not involved |
| 3. | Good is actually sold | Good remains in the owner ship of the seller |
| 4. | In case of payment defaults bank can not repossess the good | I case of payment defaults seller can repossess the good |
| 5. | Suitable for goods with no second hand value | Suitable for goods with good second hand value |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Customer Credit
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| To the Economy | |
| 1. Encourages the sale of expensive goods. | 1. Can cause general increase in price level. |
| To the Seller | |
| 1. Increases turnover and thus profit. | 1. If seller finances the installment-buying then capital requirement is increased. |
| 2. Enables stocks to be cleared. So less risk of stock going out-of-date. | 2. If buyer defaults in making payment then seller has to re possess the goods which may be damaged. |
| 3. Can earn interest if he is also financing. | 3. Administrative expense to record installments. |
| To the Buyer | |
| 1. Raises the standard of living. | Has to pay extra interest. |
| 2. It is a way of forced saving. | 2. Encourages people to spend rashly. |