Air and Water
Water:
Water is perhaps the most known substance. This is perhaps because of its abundance and numerous uses. Water is, H2O, is the most popular solvent for chemical reaction.
Tests for Water:
There are several tests for water, the easiest one which you can perform at home is physical and doesn’t involve any reaction. It is testing its boiling point. Pure water boils at 100°C sharply, and freezes at 0°C sharply.
 |
There are chemical reactions which could be applied to test for water. For example if you add water to anhydrous copper sulphate powder which is white in colour, it forms a blue solution and may | |
give heat out. If you crystallise the solution you will obtain blue crystals of hydrated copper sulphate (see the picture on the left). Another test for water is adding it to anhydrous cobalt chloride which is blue in colour, if water is added to it the anhydrous salt forms a pink solution. If you crystallise the solution of cobalt |
 |
|
| chloride you will obtain pink hydrated cobalt chloride crystals (see the picture on the right). | ||
Uses of Water:
The uses of water are many, from drinking and cleaning to irrigating crops and landscapes. Water is used for cooling, for recreation, and dust control. Water is needed for restaurants, most industrial processes, and even some religious ceremonies. On another level, the splash and flow of water in streams and fountains soothes and inspires.
In one way or another, water is a part of almost everything humans make and do. Washing a load of laundry uses 40 gallons, filling a backyard pool takes about 25,000 gallons, growing a pound of cotton consumes 1,000 gallons, while producing a pound of copper uses 20 gallons.
Uses where water is consumed, usually through evaporation or plant growth, are consumptive uses. Examples include water used for irrigation or in evaporative coolers. Non-consumptive uses, such as bathing, hydropower generation and recreation, do no t use up water. Used non-consumptively, the same water can be used again and again, although some uses lower the quality of the water. Once used, wastewater can be treated and used again as reclaimed water or effluent.
The main categories of water use are agricultural, municipal and industrial. Municipal and industrial uses currently are much less, but are growing rapidly. Mining activities and cooling towers used for power generation account for most of the remaining water use.
Water Purification:
Water that exists naturally in earth is never pure. There are always impurities in it, sometimes in large amounts. In fact water could very well be contaminated with diseases and bacteria. This is why water has to be purified before it is put to use. Water purification involves two processes (Filtration & Chlorination) done in several steps:
- Water is taken from reservoirs or any other source to the water treatment plant
- Water is passed through filters to remove large, floating objects such as pieces of rocks or mud
- Smaller particles are removed by adding aluminum sulfate which makes them stick together in large pieces and settle down
- Water is passed through sand and gravel filters which filter off small particles and may kill some bacteria (filtration is done)
- Chlorine gas is bubbled through the water to kill all bacteria living in the water making the water sterile
- The water may end to be slightly acidic, small amounts of sodium hydroxide are added to treat this. Fluoride might be added to because it helps in preventing tooth decay
- Water is then delivered to homes
Air:
Air is a mixture of gases that makes up the atmosphere of earth.
Composition of Clean Air:
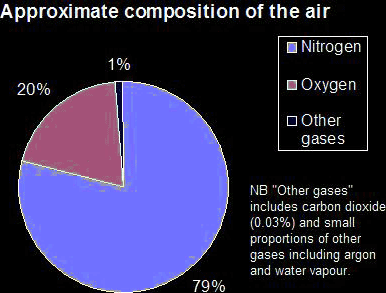
Clean air is made up of nitrogen, oxygen and traces of other gases including carbon dioxide and noble gases. There are also traces of water vapor in air. Noble gases present in air are mostly argon and some helium, neon, krypton and xenon.
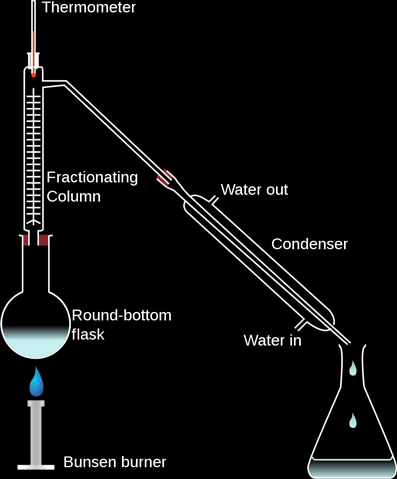
Fractional Distillation of Liquid Air:
Fractional distillation of liquid air is used to separate gases of air, specially nitrogen and oxygen. Like fractional distillation of petroleum, it is based on the boiling points of the components of air.
| GAS | Boiling Point: | Percentage Of Air |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Dioxide | -32 °C | <1% |
| Xenon | -108 °C | <1% |
| Krypton | -153 °C | <1% |
| Oxygen | -183 °C | 20% |
| Argon | -186 °C | <1% |
| Nitrogen | -196 °C | 79% |
| Neon | -246 °C | <1% |
| Helium | -249 °C | <1% |
|
 |
Air Pollution:
Pollution is the presence of harmful substances. Air pollution is the presence of pollutant gases in the air. A pollutant is a substance that causes pollution. These are:
- Carbon monoxide
- Oxides of nitrogen
- Sulphur dioxide
- Lead compounds
Carbon Monoxide: Carbon monoxide (CO) is one of the poisonous pollutants of air. It is considered a pollutant because it can kill living organisms. The main source of carbon monoxide is factories which burn carbon-containing fossil fuels since CO is one of the products of the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels. Carbon monoxide could be treated by installing catalytic converters in chimneys of the factories.
Sulphur Dioxide: Sulphur dioxide (SO2) is considered a pollutant since it contributes to acidic rain. Sulphur dioxide is a product of two process, these are combustion of sulphur –containing fossil fuels and extraction of metals from their sulphide ores (such as zinc sulphide). The problem associated with sulphur dioxide is that when it rises in the air from chimneys of factories, it mixes with water vapour of clouds and air. This results in the formation of sulphuric acid (H2SO4). When it rains, rain water which falls becomes acidic. Acid rain causes death to water creatures since it makes water acidic, acidifies soil causing death to plants and deforestation, reacting with limestone from buildings and sculptures corroding it, and may also cause lung cancer. Sulphur dioxide could be treated before it leaves chimneys of factories by reacting it with limestone which is a neutralisation reaction. This process is called desulphurisation.
SO2 + CaCO3 → CaSO3 + CO2
Oxides of Nitrogen (NO & NO2): Nitrogen oxides are formed at high temperatures as a result of nitrogen and oxygen reacting. In cars, engines have a very high temperature; this creates a chance for nitrogen and oxygen present in air in the engine to react forming nitrogen monoxide.
N2 + O2 → 2NO
The produced carbon monoxide is released through the exhaust with other waste fumes. Nitrogen monoxide reacts with more oxygen from air producing nitrogen dioxide.
2NO + O2 → 2NO2
The problem associated with nitrogen dioxide is similar to that of sulphur dioxide. It rises up in the air and mixes with rain water forming nitric acid. This causes acid rain. Nitrogen oxides can also cause health respiratory problems to humans and animals. To treat this issue, cars are now fitted with devices called catalytic converters which eliminate nitrogen oxides.
Lead Compounds: Compounds of lead are waste products of fuel burning in cars. They are considered pollutants because they are poisonous and they are said to cause mental disabilities to young children. To treat this problem, gas stations now provide unleaded fuel.
Catalytic Converters:
Car fuels contain carbon; so carbon monoxide gas is released by cars as waste fumes, as well as nitrogen oxides. These are pollutant gases. To prevent these gases from polluting air, a device called catalytic converter is fitted at the end of the exhaust. This device contains a catalyst which catalyses the reaction between these two gases producing two harmless gases, nitrogen and carbon dioxide:
2NO + 2CO → 2CO2 + N2
2NO2 + 4CO → 4CO2 + N2
The catalyst of the device works best at temperature around 200°C.
The Carbon Cycle:
The carbon cycle is a natural global cycle of the element carbon. It is what maintains a constant level of carbon dioxide in air (0.03%). The cycle goes as follows:
- Plants absorb carbon dioxide from air and undergo photosynthesis reaction which turns it into glucose and produces
oxygen: 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2 - The carbon is now stored in plants as glucose. One of two things happen, either the plants get eaten by animals or humans, or the plant dies and decays.
- If the plant is eaten by animals or humans, glucose in the plant is used by them in a process called respiration to release energy for their body.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
Respiration is the opposite of photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide is one of the products of it, which is released by the humans through breathing into the air. Thus carbon dioxide returns to the atmosphere. - If the plant dies. It is buried underground and by time it decays forming coal and other fossil fuels. These substances contain the carbon which was made and stored by the plants and they are then taken by power stations which put them to use.
- Power stations burn carbon-containing fuels that were obtained as coal or fossil fuels formed by dead plants. This is a combustion reaction.
C + O2 → CO2
Carbon dioxide is result of these reactions. Carbon dioxide produced is released to the air through chimneys of power stations. Thus the cycle is completed and all carbon dioxide returns to the atmosphere.
Green House Gases:
The sun sends energy to the earth in two forms, light and heat. Some of the heat energy reflects back to the space, some however are trapped inside the Earth. This is caused by some gases and it is called the greenhouse effect. The main greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide and methane.
Carbon dioxide is formed in many ways. It is formed on a large scale in power stations by the combustion of carbon containing fuels. Carbon dioxide is also caused by respiration of living organisms. The gas can also be produced by a reaction between an acid and a carbonate, like that of the corrosion limestone.
Methane, the other greenhouse gas is formed by animals. When animals eat and digest their food, methane gas is one of the waste products of this process. It is released to the atmosphere by animals. When plants die and decompose over many years, methane gas is also produced.
The greenhouse effect poses a threat to the world now days. This is because greenhouse gases, especially carbon dioxide, have increased in amounts in the atmosphere due to activity of humans. Lots of fuel combustion is taking place around the world, increasing the levels of CO2, while trees are being chopped off to made use of instead of leaving to replace CO2 with oxygen. These activities cause an increase of the levels of CO2 in the atmosphere, which leads to more heat trapping in earth. This rises the global temperature of the earth causing what’s called global warming.
Global warming is the increase of the temperature of the earth due to the increase of levels of greenhouse gases. Global warming has effects on the earth. To start with, it north and south poles, which are made of ice, will start to melt raising sea levels. The sea temperature will also rise causing death to marine lives. This is also accompanied by other natural disasters such as hurricanes and heavy rains.
Humans could prevent this by reducing combustion of fossil fuels and leaving forests to live.
Rusting:
Rusting is the corrosion of iron as a result of reaction with oxygen from air and water. If iron objects are left uncovered and exposed to air & water, iron will react with oxygen forming hydrated iron oxide (also known as rust). Rust is a reddish brown flaky solid which will fall of the object making it thinner and loses it its shape. Iron must come in contact with air and water in order for rusting to happen. The formula of rust is Fe2O3. xH2O. Steel can also rust since it is made up of mostly iron.
Rusting can become very dangerous in some cases. For example, bridges that cross rivers stand on columns that are made of iron. The conditions of rusting are present in this case (Water from the river and oxygen from the air). There is a risk that the columns will rust and collapse with the whole bridge. In another case, ships are made of iron. Again, the conditions of rusting are present (water from the sea and oxygen from the air). In fact, this situation is more critical because sea water contains minerals that act as a catalyst to speed up the reaction of rusting.
There some available methods to prevent rusting. These methods are based on covering the iron object with another substance to create a barrier between iron and oxygen and water so that rusting does not take place:
Painting: The iron or steel object is painted all over. The paint creates the desired barrier to prevent iron or steel coming in contact with air and water. This method is used in car bodies and bridges.
Electroplating: The iron or steel object gets electroplated with another metal that doesn’t corrode. The object is usually electroplated with tin or chromium since they are very unreactive. This method is used in food cans and car bumpers.
Sacrificial Protection: This method is based on the idea that metals that are higher than iron in the reactivity series will react in preference to it and thus that metal is corroded and the iron is protected. Metals usually used as protectors in this method are zinc and magnesium since they are higher than iron in the reactivity series. In ships for example, zinc or magnesium bars are attached to the iron base of the ship which is in contact with water and oxygen from air. But rusting doesn’t take place since zinc or magnesium is the one that gets corroded. These bars must be replaced from time to time because once they all get corroded, iron becomes unprotected and rusts. This method is usually used in ships or bridge columns. The zinc or magnesium bars do not have to completely cover the iron or steel because as long as they are attached to each other the zinc or magnesium bars get corroded and not the iron.
Galvanisation: Galvanisation is a very reliable method for preventing rusting. It is basically covering the whole object by a protective layer of zinc. This can be done either by electroplating the object with zinc or dipping it into molten zinc. The zinc layer provides a barrier that prevents iron or steel from coming in contact with air and water. The zinc gets corroded instead iron thus protecting it. If the a part of the zinc coat falls off and the iron or steel gets exposed to air and water, the bare part still doesn’t get corroded since it is protected by sacrificial protection now.