Nutrition
Nutrition is taking in nutrients which are organic substances and mineral ions, containing raw materials and energy for growth and tissue repair, absorbing and assimilating them. Nutrition is one of the characteristics of living organisms. All organisms do it, they do it to obtain energy for vital activities and raw materials needed for growth and repair.
Every Individual needs to take in a certain amount of each nutrient daily, depending on their age, size, sex and activity. There are 7 Types of nutrients, these are:
|
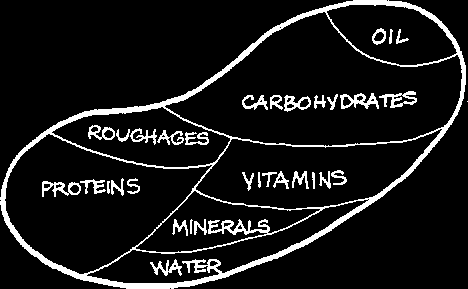 |
Carbohydrates, proteins, fats and vitamins are all organic substances. This means that they are made by living organisms (plants) and contain carbon atoms in their structures. Plants make organic substances from inorganic materials like carbon dioxide, water and inorganic minerals. Animals are unable to do this.
Carbohydrates:
This nutrient is an organic compound composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Function:
It is used as an energy resource, essential in respiration to release energy.
It is used in creating the cellulose, the substance forming cell walls of plant cells.
Carbohydrates are 3 types:
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
Monosaccharide and Disaccharides are sugars, they are reducing for Benedict’s reagent, except for the disaccharide sucrose, it is non-reducing.
Polysaccharides are not considered as sugars and don’t have a sweet taste. Excess polysaccharides are stored in the liver and muscles.
Lipids (Fats):
These are composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. But their ratios are different than that of carbohydrates. One fat molecule is made of a glycerol unit and three molecules of fatty acids.
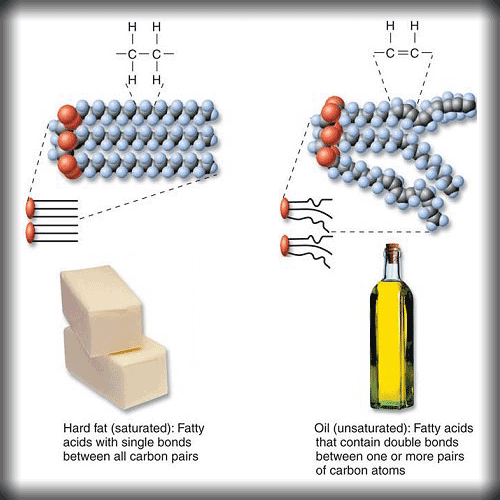
Fats are essential in a diet because they are needed to:
- Release high amounts of energy
- Make cell membranes
- Store them under the skin to insulate heat.
- Forming a layer of fats around organs to protect them from damage
- Storing energy (better than glycogen)
When fats are respired, they produce about twice as much energy as carbohydrates.
Proteins:
These are also organic compounds; they contain the elements Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen and sometimes Phosphorus or Sulfur.
A molecule of protein is a long chain of simpler units called amino acids.
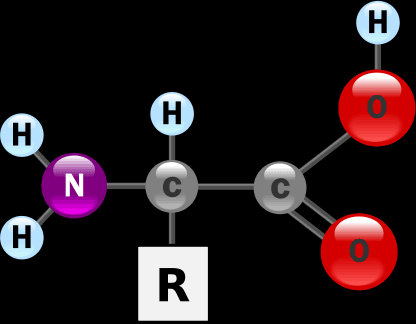
These amino acids are linked together by what's called “peptide bond”.
Types of protein:
- Animal Protein: It contains the most biological value because it contains all essential amino acids (Meat, Milk, Fish, Eggs etc).
- Plant Protein: It contains a lower biological value to humans because it contains fewer essential amino acids (Cereals, Peas, Beans etc).
Needs of proteins:
- Making and new body cells
- Growth and repair
- Making enzymes (they are proteins in nature)
- Build up hormones
- Making antibodies
Although proteins are needed in high amounts, the body will only absorb as much as needed, so excess protein is delaminated in the liver and excreted as urea.
Vitamins:These are organic, soluble substances that should be present in small amount in our diets, they are very important though. Most of the amount of vitamins in our bodies was taken in as nutrients, the body its self can only make few Vitamins, so we have to have to get them from organisms that make them, such as plants. Each type of Vitamin helps in chemical reactions that take place in our cells. Types Of Vitamins:Vitamin C: This is present in most fruits and vegetables specially citrus fruits like lemon and oranges, however, it is damaged by heating so it these foods have no value of Vitamin |
 |
 |
C if they are eaten cooked. Vitamin C is essential for the formation of Collagen, a protein that functions as cementing layer between cells, Vitamin C also increases immunity. Vitamin D: This is present in fish oils, egg yolk, milk and liver. Unlike Vitamin C, Vitamin D is made by animals as well as plants, this occurs when the skin is exposed to the Ultra Violet Rays of the sun. Vitamin D plays a big role in absorbing Calcium from the small intestine and depositing it in bones. So it is responsible for having healthy bones. |
Minerals (Inorganic Ions):
These are a lot of types, each needed in small quantities. Iron and Calcium are the most important minerals, and they are needed in higher amounts.
Types Of Minerals:
- Calcium: This mineral is needed for the formation of bones and teeth as they are made of calcium salts, it also helps in blood clotting and transmission of nerve impulses. Good sources of the mineral Calcium are milk, dairy products and hard water.
- Iron: This mineral is needed for the formation of the red pigment haemoglobin which is essential for the transport of oxygen around the body in red blood cells. Good sources of Iron include red meat specially liver and green leafy vegetables.
Roughages (Fibre):
Although roughages are not even absorbed by the body, they are a very important nutrient in our diet. Roughages are mostly cellulose, which is the substance that makes up the cell walls of plants we eat. We humans, have no enzyme that could digest cellulose, that means that roughages enter the body from the mouth, go through the digestive system, and out through the anus unchanged. But as it goes through the digestive system, roughages take space in the gut to give the gut muscles something to push against, this process of pushing the food through the gut is called peristalsis, without roughages peristalsis is very slow and weak. Quick and strong peristalsis means that food stays in the alimentary canal for a shorter period, this prevents harmful chemicals of certain foods from changing the DNA of cells of the alimentary canal causing cancer, so roughages also helps stay away from cancer. Roughages are found in leafy vegetables.
Water:
About 70% of your weight is water. Water is perhaps a very essential nutrient we should take in. The functions of water include:
|
 |
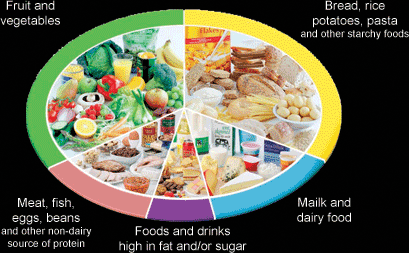 |
Balanced Diet:A perfect diet contains all of the nutrients in reasonable proportions, not too much and not too little. The perfect diet should also contain energy as much as the total energy used by the individual. Unbalanced Diet (Malnutrition):Malnutrition is eating inadequate proportions of food. In other words, an unbalanced diet means it is rich in a nutrient and low in another, or even lacking of a substance. There are lots of effects of malnutrition, such as starvation, obesity or deficiency diseases. |
Starvation:
Starvationis a severe reduction in vitamin, nutrient and energy intake. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, death. The term inanition refers to the symptoms and effects of starvation. In case of starvation the body tends to feed on its own self. When the glucose level is decreased in the body, the liver breaks down fats to respire for energy, when the body is out of fats, it starts respiring proteins from the muscles to release energy.
Obesity:
is the opposite of starvation. It is eating too much of every nutrient, especially carbohydrates and fats. Obesity doesn’t strike alone, it brings with it several other diseases such as high blood pressure, cardiac diseases, diabetes, stress on joints and bones as well as other psychological issues like low self esteem and lack of confidence. To prevent obesity, you have to control your carbohydrates and fats intake and exercise regularly.
Another consequence of malnutrition is deficiency diseases.
These are results of a certain nutrient in the diet:
- Scurvy is the deficiency disease of vitamin C. Its symptoms include bleeding gums.
- Rickets is the deficiency disease of both Vitamin D and Calcium. Bones are made of calcium which Vitamin D helps in depositing in the bones, if any of both is lacking in the diet, rickets is developed.
- Anemia is the deficiency disease of iron. The amount of haemoglobin decreases causes short breath and tiredness.
- Kwashiorkor affects children whose diets are lacking in protein. It causes weakness and tiredness.
Special Needs:
There are certain types of people whose diets need to be different to normal ones.
Such as pregnant women, breast-feeding women or children going through puberty.
Pregnant Women:
The diet of a pregnant woman needs to be very rich of certain nutrients because she is not only feeding her self, she is feeding her baby as well. In order for the fetus to develop well, it needs extra Protein, Iron, Calcium and Vitamin D. Proteins are to develop the tissues of the fetus, Iron is to make haemoglobin and to store in the liver, while Calcium and Vitamin D are to develop the baby’s bones.
Breast-Feeding Women (Lactation):
Lactation means the production of breast milk. After pregnancy, the mother breast-feeds the baby for about 6 months or more. Breast milk needs to be high in Proteins, Calcium, and Vitamins to guarantee a healthy growth for the infant.
Growing Children (Passing Puberty):
At some point, each child gets a growing spurt. This is a very high growth rate that increases the child’s size and mass in a short period of time. A growing child’s diet needs extra Proteins to develop cells and enzymes because their metabolic rate is higher, Calcium and Vitamin D to develop bones and Iron to make hemoglobin.
Food Additives:
These are chemical compounded added to foods by the manufacturer because they have some benefits such as increasing the lifespan, prevent rotting etc.
Most food additives are good, such as ones that add colors or flavors to foods. But there are others which have been proven hazardous to humans.
Good food additives include flavorings and colorings which are used to make the food more appealing, antioxidants which prevent foods from combining with oxygen and rot, and stabilizers which stops foods like ice-cream from separating into water and fatty components.
Food preservatives though, are a widely used food additives which increase the lifespan of foods, making it cheaper to store and transport. However, scientists claim that some preservatives contain nitrites which combine with chemicals making a substance (nitrosamines) that causes cancer in animals.
| Food Additives | |
|
|
Microorganisms And Food Industry:
Production of Single Celled Protein (Mycoprotein):
Mycoprotein is a protein made from microscopic fungus. Humans need large amounts of proteins in their diets, in some poor areas, sources of proteins like meat are unaffordable, mycoprotein is used.
The process takes place in a sterilised container called fermenter. The micro-organisms are grown in the fermenter and supplied with air which contains oxygen for aerobic respiration, ammonia as a source of nitrogen to be used by the micro-organisms to make proteins, and methanol which contains carbon for the formation of carbohydrates.
Advantages of mycoproteins are that it is cheaper than any source of protein but equal in value, and that it contains much less fats and more roughages and carbohydrates
Production Of Yoghurt:
- Milk is sterilised by boiling
- Certain types Bacteria are added to the milk
- The milk is kept warm to provide best conditions for bacteria growing
- Bacteria respire producing lactic acid, thickening the milk and giving it the pleasant flavour
- Yoghurt is cooled and flavours or fruits could be added.
Food Tests:
Starch Test:
- Put sample in a test tube
- Add water to make it a solution
- Add iodine solution
- Is starch is present the solution changes colour from yellowish brown to Blue Black.
- If starch is not present the solution remains yellowish brown.
Reducing sugars (carbohydrates) test:
Note: This test is only applicable on all sugars (monosaccharide and disaccharide) EXCEPT FOR SUCROSE.
- Add sample to a test tube
- Add Benedict’s Reagent
- Put test tube in water bath for heating
- If reducing sugars are present the solution turns from blue to yellow,orange,red (fire colours)
- If reducing sugars are not present the solution remains blue.
Proteins Test:
- Put sample in a test tube
- Add water to make a solution
- Add Buiret Reagent
- If proteins are present in the solution turns Purple
- If proteins are not present the solution remains blue.
Note: Biuret Reagent is blue in colour and made of copper sulphate and a small amount of sodium hydroxide.
Fats Test:
- Add sample to a test tube
- Add ethanol
- Add water and shake well
- If fats are present the solution becomes unclear
- If fats are not present the solution remains clear
General Table:
Nutrient |
Test |
Colour |
Positive |
Negative |
Starch |
Iodine sol. |
Yellow / Brown |
Blue / Black |
Yellow / Brown |
Carbs |
Benedict’s |
Blue |
Red (fire) |
Blue |
Proteins |
Biuret reagent |
Blue |
Purple |
Blue |
Fats |
Ethanol/water |
- |
Cloudy |
Clear |