Enzymes
What are enzymes?Enzymes are proteins that function as a biological catalyst. A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction but isn’t changed by the reaction. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a substance that decomposes into Water (H2O) and Oxygen (O2) if it is left in room temperature for a period of time. This reaction could a long time, but it could be sped up if we add a catalyst. Each catalyst can catalyse a specific substance and nothing but it. The catalyst for Hydrogen peroxide is called Manganese4 oxide. If it is added we will get water and oxygen gas in a very short time, and the manganese4 oxide could be obtained again as it was, it remains unchanged. |
 |
How Do Enzymes Work?
Enzymes work the same way as catalysts do, they can work with only one substrate and they can be used more than once.
Enzymes have a structure that is called active site. Only one substance can fit into the active site to be digested, and it is the only substrate that this particular enzyme works with.
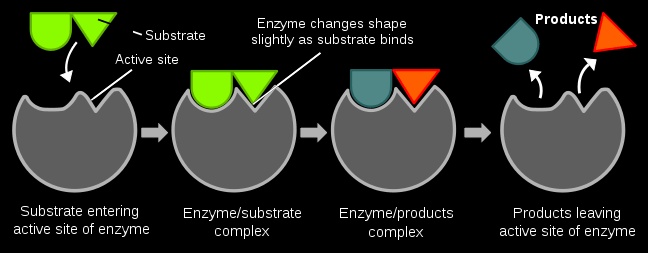
The figure above shows the function of enzymes:
- The substrate enters the active site of the enzyme.
- The reaction takes place.
- The substrate exits the enzyme as two simpler products.
You can also think of the way enzymes work as a key and a lock, the key is the substrate and the lock is the enzyme. The key should be exactly the right shape to fit in the lock, so does the substrate to fit in the active site of the enzyme. The key could only open only one lock, and the lock could be unlocked by only that key.
Enzymes are two types, Builders and Breakers. Builder enzymes do the opposite of breaker enzymes. Breakers break large molecules into smaller simpler ones, builders combine smaller ones to make large molecules.
Breaker enzymes are used in the digestive system to break down large insoluble molecules into simpler soluble ones to be used by the body. They are also present in cells that respire to break down sugars and oxygen into carbon dioxide, water and energy. Builder enzymes are present in plants to be used in photosynthesis, the opposite of respiration, in photosynthesis, oxygen and water are combined together to form carbon dioxide and sugars.
Naming enzymes depends on the substrate they work on. For example:
The sucrase enzyme works on sucrose.
The maltase enzyme works on maltose.
Enzymes are reusable and are only affected by the change in temperature and pH.
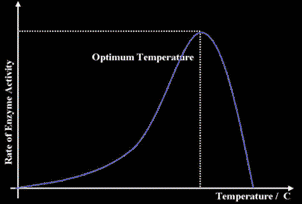
Affect of temperature on the enzyme’s activity:
Each enzyme has an optimum temperature, this is the temperature at which the enzyme is most active, below this temperature the activity of the enzyme decreases until it becomes inactive at low temperatures, above this optimum temperature the enzyme becomes denatured and can no longer work.
At low temperatures the enzyme is and the substrate are moving very slowly and collide weakly, the enzyme is said to be inactive and doesn’t work. As the temperature increases, the enzyme and substrate gain more kinetic energy and move faster colliding more, the enzyme becomes more active and the reaction takes place. When the enzyme reaches it’s optimum temperature, it is in its most active mood, if the temperature crosses the optimum the enzyme begins to die and become denatured. The enzymes become denatured when the shape of their active site changes as a result of high temperature, thus the substrate cannot fit into the active site and the enzyme is useless.
Each enzyme has its own optimum temperature, enzymes in humans have optimum temperatures of around 40 degrees. Plants have enzymes with optimum temperature of about 25 degrees.
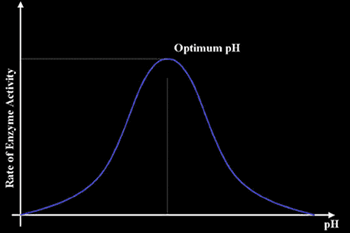
The Effect of pH on the enzyme’s activity:
As in temperature, enzymes have an optimum pH. The pH is a scale measuring the acidity or alkalinity of a substance or solution. The scale runs from 1 to 14. pH 7 is neutral, below that it is acidic and above that it is alkaline.
Each enzyme has an optimum pH, if this pH changes, the shape of the active site of the enzyme is changed, thus the substrate will not be able to fit in it, and the enzyme becomes useless.
Uses Of Enzymes In Seeds Germination:
Seeds grow into plants by germinating. Seed germination involves enzymes breaking the materials stored in the seed down to be used in growth, energy and building cells. The seed contains stored substances such as:
- Starch: Starch is broken down by amylase enzyme into maltose, maltose is then broken down by maltase enzyme into glucose which is used in respiration.
- Proteins: Proteins are broken down into amino acids by Protease enzyme, amino acids are used in building up cells and growth.
- Fats: Fats are broken down into fatty acids by lipase enzyme, they are used in making cell membranes.
In order for a seed to germinate, some conditions must be present:
- Water: To activate the enzymes.
- Oxygen: To be used for respiration.
- Warm Temperature: For providing the best conditions for enzymes to work and optimum temperature.
Uses Of Enzymes In Biological Washing Powders:
Washing powders contain detergents that help in cleaning clothes by dissolving stains in water. Some stains are made of insoluble substance, these cannot be removed by normal washing powders, instead, a biological washing powder is used. Biological washing powders contain enzymes that break down the insoluble stain into smaller soluble substances, which are then dissolved in the water. For example, if your shirt gets stained by egg yolk or blood, there is an enzyme called protease in the washing powder that will break down the insoluble protein into amino acids, which are dissolved in the water and sucked away. Thus the shirt becomes clean. |
 |
The best removal of stains is maintained by providing the optimum temperature for enzymes, presoaking to leave time for the enzymes to digest, putting the suitable amount of the powder.
Use Of Enzymes In Food Industry:
Enzymes are often used in the manufacturing of different foods.
Baking – Brewing – Cheese Making:In baking, both yeast and sugar are used. Yeast cells contain enzymes that ferment sugar by anaerobic respiration producing carbon dioxide bubbles which causes the dough to rise as in the photo. Brewing is the process of making wine or beer. In this process fermentation is Involved producing alcohol which and carbon dioxide that gives wine and beer its sparkle. In making cheese, an enzyme called rennin extracted in enzymes, helps by clotting milk. |
 |
Making Juices:In fruits such as apples or oranges, a substance called pectin holds the cells together making it |
 |
Making Baby Foods:
It is hard for new born babies to digest food such as high protein foods. That is why foods like that are treated with proteases to break down protein to amino acids, making it easier for newborns to absorb and assimilate them.
Making Sugar:
Sugar producing companies get sugar from starch by using the amylase enzyme to digest starch into maltose. For dieters a sugar called fructose is very useful because it provides a sweater taste than other sugars from a less quantity. Fructose can be obtained by using the isomerase enzyme to convert glucose to fructose.
Meat And Leather Production:
Proteases are used to make meat less tough and acceptable for consumers by treating cuts of meat.
In leather industries hairs are removed from animal skin by digesting them using protease enzymes.
Enzymes Extraction:
The Enzymes used in the industries are taken from either fungi or bacteria. This takes place in a Fermenter, this is a large sterilized container with a stirrer, a pipe to add feedstock and air pipes.
The following steps take place:
- The micro-organisms and the feedstock are added and the liquid is maintained at 26 degrees and pH of 5-6.
- The micro-organisms produce two types of enzymes, either extra-cellular or intra-cellular.
- Extra-cellular enzymes are extracted from the feedstock by filtering.
- Intra-cellular enzymes are extracted by filtering the micro-organisms from the feedstock, crushing them, wash them with water then extracting them from the solution.
Enzymes And Antibiotics:
Antibiotics are powerful medicines that fight bacterial infections. Micro-organisms are used for the production of antibiotics.
Some Antibiotics, like bactericides, fight bacteria by damaging its cell walls causing them to burst and die. Other antibiotics interfere with the protein synthesis and stop the bacteria growing.
Antibiotics have no effect on human cells because human cells have no cell walls and the structures involved in protein production are different than that of bacteria.
Antibiotics are obtained from sources like:
- Bacteria (Actinobacterium Streptomyces): this bacterium produces the antibiotic strepmycin.
- Fungi (Penecillum fungus): penicillin, the first antibiotic discovered is produced by thing fungus.
Different types of penicillin are produced by different species of the fungus. They are chemically altered in lab to make them more effective and make them able to work with different diseases.
Steps of production:
- The Fermenting tank in filled with nutrient solution of sugar (lactose) or corn liquor which contain sugars and amino acids,
- Minerals are added,
- pH is adjusted around 5 or 6,
- Temperature is adjusted about 26 degrees,
- The liquid is stirred and air is blown through it,
- The micro-organisms are added and allowed to grow for a day or two in sterile conditions,
- When the nutrient supply is decreased, micro-organisms secrete their antibiotics,
- The fluid containing the antibiotic is filtered off and the antibiotic is extracted.