Classification
Classification is the sorting out of living organisms according to common features.
The classificatory system:

The biggest group is the Kingdom, Kingdoms are divided into Phyla which are divided into Classes which are divided into orders which are divided into families which are divided into genera which are divided into species.
Species: A group of living organisms having the same characters and can breed together successfully producing a fertile offspring.
As we go down the classificatory system, organisms number decrease. The system can be memorized by
the word “KPCOF” but don’t forget get adding genus and species at the end.
The Binomial System:
Each organism has two names written in Latin, the first name is the name of the genus it belongs to and the second name is the name of its species. This is the binomial system
However, we don’t just write names as we do usually, there are certain rules that must be followed to write the Latin name:
- The name of the genus must begin with a capital letter.
- The name of the species must begin with a small letter.
- Both names must be written in Italics or if you can’t write in italics just Underline the name.
Other examples:
- Wolf: Canis lupus
- Zebra: Equus burchelli
- Lion: Panthera Leo
Viruses:
Viruses are not classified into a kingdom because it is not considered a living organism because it cannot reproduce on its own.They are very small and measured in nm (nanometers), they could only be seen through an electronic microscope.
A Virus has a protein coat around it, and genetic material inside it (RNA or DNA).
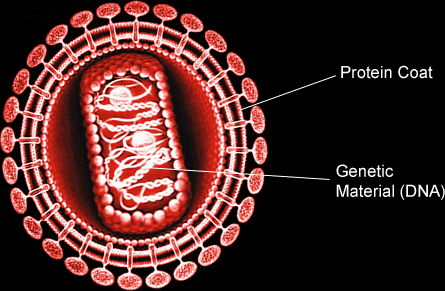
Viruses are not considered a living organism because they don’t have any of the seven characteristics, except that they reproduce by replication, but that only happens inside the host cell.
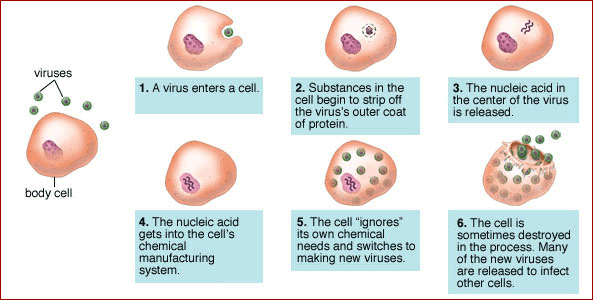
Viruses strike humans by the following steps:
- A virus sticks its self to a cell and injects the genetic material into the it
- The virus reproduces more of its self by replication
- The virus keeps on replicating until the cell bursts
- The new viruses go out and kill other cells
Kingdom Bacteria:
A bacterium is a single-celled organism that lives everywhere on earth. It can only be seen by a microscope
Structure of bacteria:
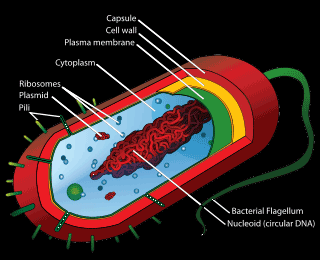
Cell Wall: It’s made of a substance called peptidoglycan, which contains glycogen and sugars.
Cell Membrane: It protects the bacterium from bursting when too much water is present and gives it its shape.
Cytoplasm: It’s where the chromosomes are kept and it stores granules of various materials.
Chromosome: A single DNA strand coiled up, it contains the bacterium’s genes.
Slime Capsule: This is an extra feature that is not present in all bacteria, it is created by the bacterium when the external conditions are not favourable.
Flagellum: This is an extra feature that is not present in all bacteria, it helps in moving and swimming.
Adaptation:
Bacteria have managed to adapt its self in order to survive in various conditions. They obtain their food by various methods:
Autotrophic Bacteria: They make their own food by photosynthesis.
Heterotrophic Bacteria: They feed on ready made food, they are unable to create their own.
There are three types of heterotrophic bacteria, these are:
Saprophytic Bacteria: They secret enzymes which digest dead organic matter to simple soluble substances which the bacterium feeds on, thus causing Decomposition.
Mutualistic Bacteria: These live on the roots of plants, they use Nitrogen in the airspaces between the soil to convert it to nitrate ions which they feed on.
Pathogenic Bacteria: These are parasites, they cause diseases to plants and animals.
Bacteria also reproduce extremely quickly by binary fission producing numerous offspring in a short time.
Some bacteria has a flagellum which is very useful for movement and swimming.
Some bacteria respire aerobically while others respire anaerobically.
Kingdom Fungi:
Fungi are Multicellular organisms, except for yeast which is a unicellular fungus. Some fungi are not made of cells, but rather of microscopic threads called hyphae.
There are two types of hyphae:
Reproductive hyphae: They form spores which carry out reproduction.
Feeding hyphae: They form a network which grows over or through the food materials, they are called mycelium.
Hyphae are tube like, microscopic structure, it contains a cytoplasm which contains glycogen granules, and several nuclei. It doesn’t contain chloroplasts neither starch granules. In the center there is a vacuole, and the hyphae is surrounded by a hyphae wall which is sometimes made of chitin. Large numbers of hyphae grow together through whatever the fungus is feeding on making a branching network called mycelium.
How Do Fungi Eat ?
Fungi use a process called saprotrophic nutrition to feed its self. The hyphae secretes enzymes which digests dead organic matter or animal waste which is then absorbed by the hyphae to be used by the fungi.
Reproduction Of Fungi
At some point the fungi produce a reproductive structure, mushrooms for example, which produces thousands of tiny spores, these are then dispersed to other areas and grow into a new mycelium.
Adaptations Of Fungi
Fungi are adapted to perform their functions easily by the following ways:
They grow long mycelium of hyphae on whatever they feed on, these secret enzymes which digests what the fungi feeds on.
They are able to grow tall mushrooms of toadstools so the spores could be widely dispersed by wind or insects, thus they reproduce quickly.
Why Fungi Are Not Plants:
Long ago, fungi were classified as plants, but in details, fungi are actually different to plants, firstly, they do not contain chloroplasts and they do not undergo photosynthesis. Secondly, Their cell walls
(hyphae walls) are made of chitin not cellulose as in plants. Thirdly, their extra supplies of sugar is stored as glycogen not starch. And lastly, they are heterotrophic eaters not autotrophic like plants.
Kingdom Plant:
Plants are multicellular organisms. The main difference between them and other organisms is they feed using photosynthesis, which is a process which involves making sugars out of water and carbon dioxide using the sunlight energy. Plants are green because they contain a lot of chlorophyll which is a green pigment which traps sunlight for photosynthesis, plants are autotrophic organisms, they make their own food. Plant cells contain a large vacuole, a nucleus, chloroplasts and a cell wall made of cellulose, cell walls are not present in animal cells.
The Plants Kingdom contains several different phyla, but we will discuss only one of them, which is flowering plants or Angiosperms.
There are two types of flowering plants, monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous (monocots and dicots for short). The main difference between both types is the number of cotyledons in their seeds, monocots contain only one cotyledons in their seeds
while dicots contain two in theirs. Cotyledons are structures which grow into the first leaves after germination.
One could differentiate between the two classes (monocots and dicots) just by looking at their external features. Monocots have flowers with number of parts divisible by three (three petals – six leaves etc.), while dicots have number of parts of the flower divisible by 4 or 5 (4 petals – 10 leaves etc.)
 |
 |
A monocot flower, |
A dicot flower, containing 5 petals (divisible by 5 ) |
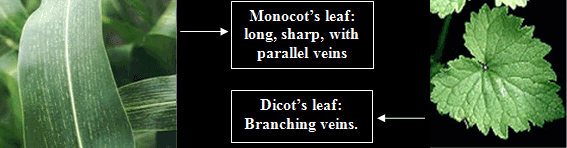
The difference could also be told by looking at the leaves of both flowers, you find that monocots have long sharp leaves with parallel veins, and dicots have leaves with branching veins.
Kingdom Animal:
The animal kingdom is divided into two groups, vertebrates and invertebrates. To study this kingdom study the following tables.
Vertebrates Phylum: Chordata
P.O.C/Class |
Fish |
Amphibia |
Reptiles |
Birds |
Mammals |
Picture |
|
|
|
|
|
Body |
Scales |
Moist Skin |
Dry Scales |
Feathers |
Fur/Hair |
Number |
2 fins |
4 limbs |
4 limbs |
4 limbs |
4 limbs |
Blood |
Cold |
Cold |
Cold |
Warm |
Warm |
Reproduction |
Lay Eggs |
Lay Eggs |
Lay Eggs |
Lay Eggs |
Give Birth |
Exta Info |
Live in water |
Live on land |
Lay water- |
Lay eggs |
Have ear |
- P.O.C = Points of comparison
- Cold Blooded = Poikilothermic – Warm Blooded = Homeothermic.
Invertebrates Phylum: Arthropoda
- All arthropods have jointed legs
- All arthropods have a hard external skeleton called CUTICLE or EXOSKELETON that encloses their body.
P.O.C/Class |
Insecta |
Arachnids |
Crustaceans |
Myriapods |
Picture |
|
|
|
|
Body |
Head |
Cephalothorax |
Cephalothorax |
Many body |
Eyes/ |
Compound |
Simple eyes |
Simple eyes |
Simple eyes |
Wings/ |
Wings |
No wings/ |
More than 4 |
No wings/ |
Extra Info |
Wings are |
Spiders and |
Live in water/ |
Millipedes |
Phylum: Molluscs:
- They have a soft body and many have a hard shell
 |
 |
 |
| Snail | Octopus | Oyster |
Phylum: Annelids:
- Some have heads and antenna
- They have legs like structures called chaetae which helps them moving
- Their body is divided into many segments
 |
 |
| Earthworm | Tube Worms |
Phylum: Nematodes:
- They are worms like Annelids
- Their body is not divided into segments
- No obvious head or legs
- No chaetae
- Some are parasites that live in the digestive system
- Some live in the soil
 |
 |
| Nematodes under microscope | |








